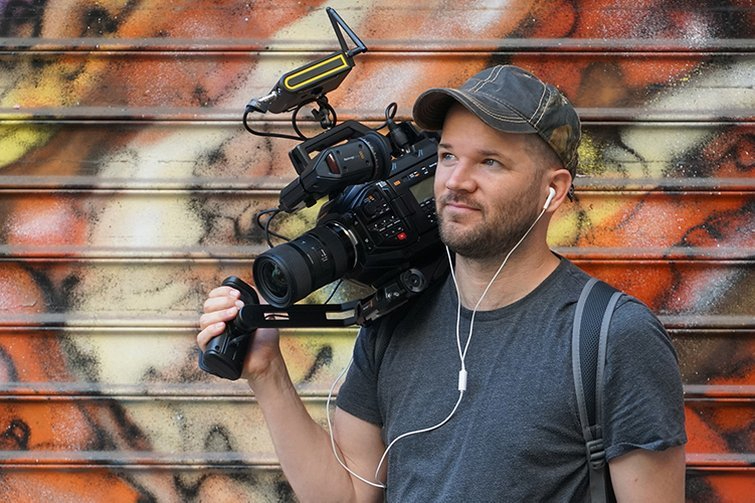
What is a Camera Operator?
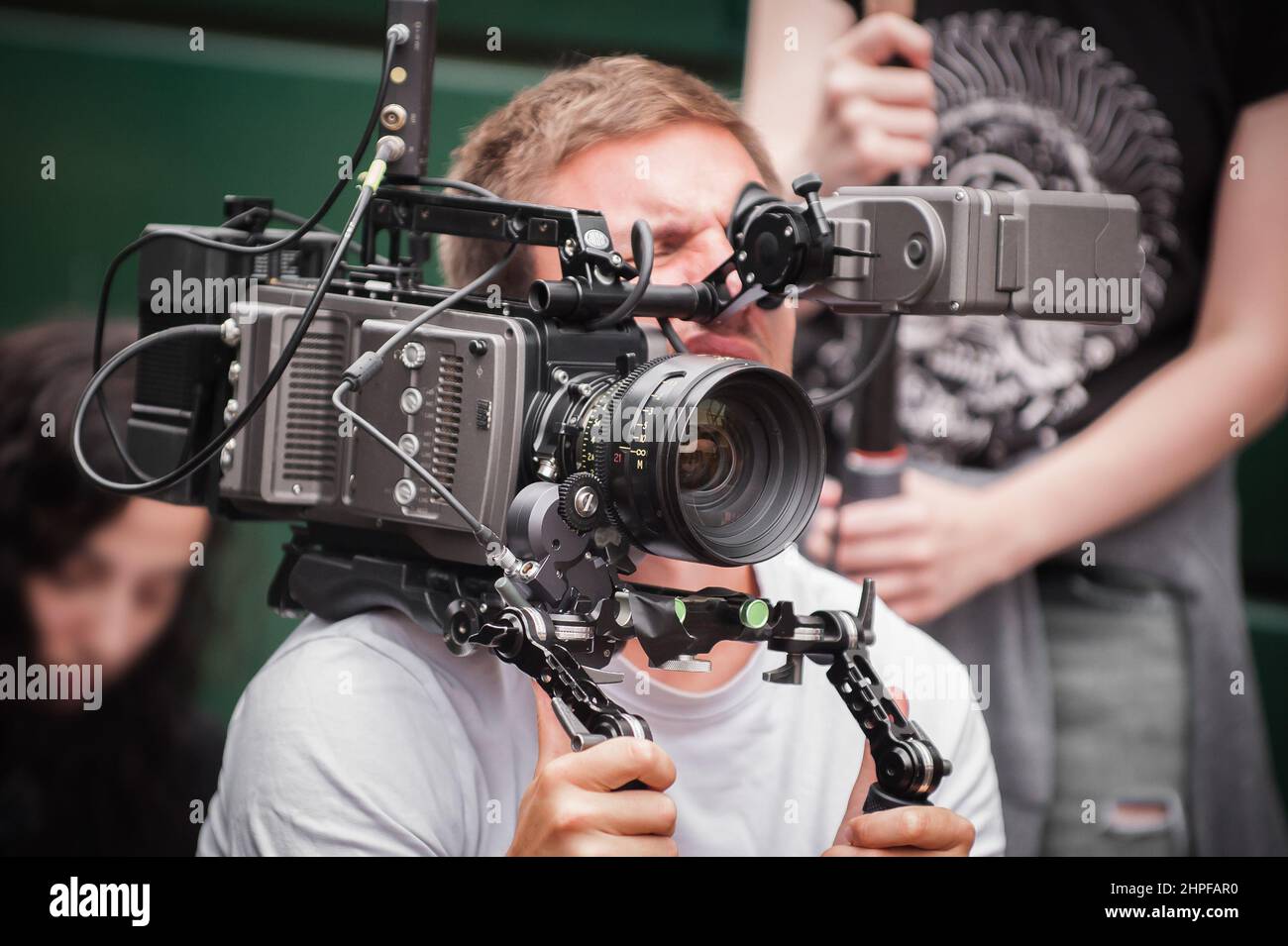
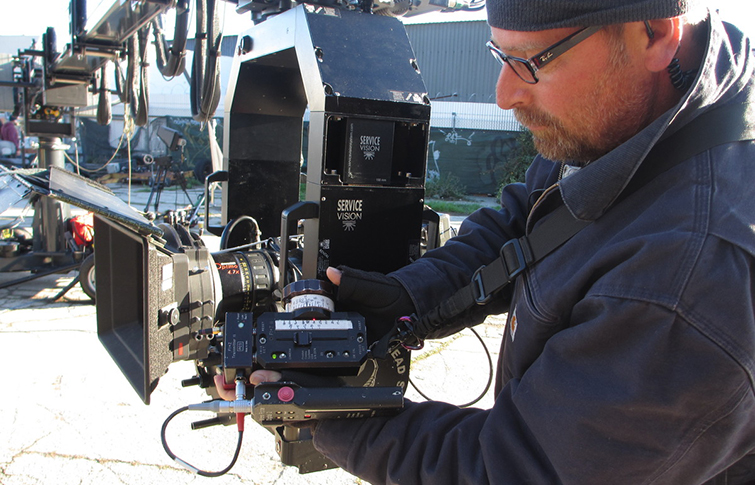
A Camera Operator is the skilled professional who physically operates the camera during filming, bringing the director's vision to life through precise movements, framing, and technical expertise.
Key Responsibilities:
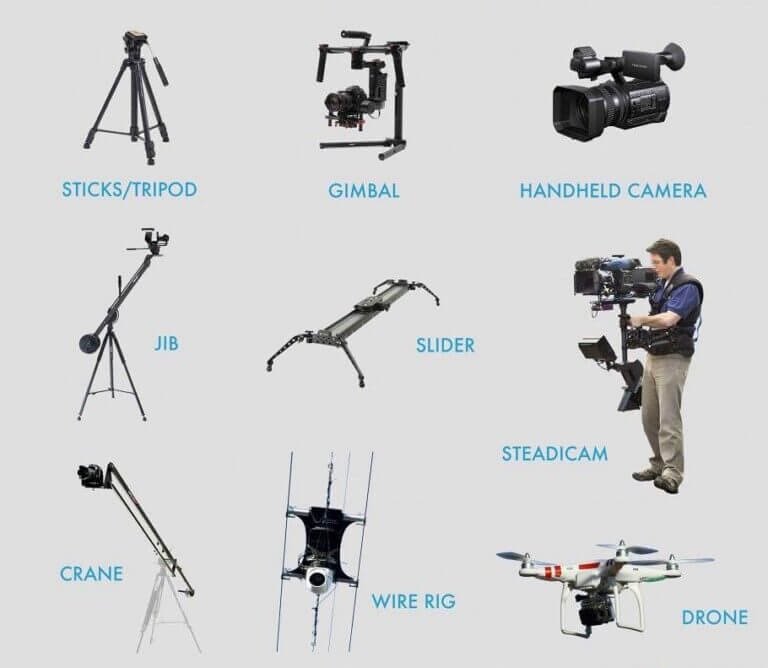
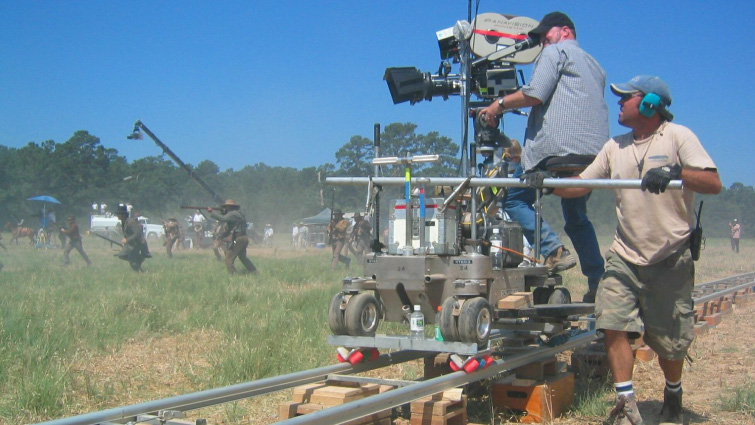
- Operating camera equipment (handheld, Steadicam, dolly, crane)
- Executing precise framing and camera movements
- Collaborating closely with the Director of Photography (DP)
- Maintaining focus and exposure during shots
- Ensuring smooth, professional camera work

Professional camera operator in action